728x90

Getting to know Your Data
Data objects and Feature Types
- Nominal - {red, blue, white,... }
- Binary - 0, 1
- Ordinal - {small, medium, large}
- Numeric
- Ratio-scaled
- Interval-scaled
Basic Statistical Description of Data
- Mean
- Median
- Mean과 달리 데이터가 추가되면 다시 계산해야 함 ➡️ interpolation으로 해결
- Mode - 가장 자주 나타나는 value
- Symmetric vs. Skewed Data - 대칭 또는 비대칭(치우쳐진) 데이터
- Quartiles, outliers and boxplots
- IQR(Inter-quartile range)
- min, Q1, median, Q3, max
- Boxplot : visualization of the above five numbers
- Outlier : 1.5*IQR 보다 크거나 작은 값들
- Variance, Standard deviation : 분산, 표준분포
Data Visualization
- Histogram
- Quantile plot
- Quantile - quantile plot
- Scatter plot
Measuring Data Similarity and Dissimilarity
- Proximity Measure for Nominal Features
- Simple Matching - 전체 중에서 몇 개가 똑같은 지
- 새로운 Binary feature를 사용해 데이터 표현하기 - red => [0,1]
- Proximity Measure for Binary Features
- symmetric - 두 데이터 결과의 중요도가 같을 때 - 0과 1이 둘 다 중요
- 전체에서 1, 1 / 0, 0 이 similar, 1, 0 / 0, 1이 dissimilar
- asymmetric - 하나가 다른 하나보다 중요할 때 - 1이 0보다 중요, (0, 0) 무시
- ((1, 0) + (0, 1)) / ((1, 1) + (1, 0) + (0, 1)) 가 dissimilar
- symmetric - 두 데이터 결과의 중요도가 같을 때 - 0과 1이 둘 다 중요
- Proximity Measure for Numeric Features
- normalize 해 줘야 함
- Minkowski Distance
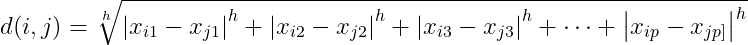
- h = 1 : Manhattan
- h = 2 : Euclidean
- h ➡️ ♾️ : Supremum
- Cosine Similarity
- Distance for Ordinal Features
- 순서가 중요하다. Rank를 숫자로 매김
- A+ : 1, A0: 2, B+: 3 이런 식으로 한 다음 normalize 시킴
Data Preprocessing
Why? Accuracy, Completeness, Consistency,...
Data Cleaning
- incomplete, noisy, inconsistent data 처리해야 함
- Missing Data - 그냥 지워버리거나, 직접 채우거나, 자동으로 평균값이나 이런 걸로 채워버리거나
- Noisy & inconsistent data - outlier detection 적용, 단위가 다른 경우, 인간이 봐야 함
Data Integration
- Handling Redundancy in Data Integration
- Correlation Analysis
- Nominal
- $X^2(chi-square) test : x^2=\sum_{each \, cell}{\frac{(Observed - Expected)^2}{Expected}}$
- 이 값이 클수록 corelated 된 것임
- Numeric
- Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC)
- $r_{A, B} = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}(a_{i}-\bar{A})(b_{i}-\bar{B})}{(n-1)\sigma _A \sigma_B} = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}((a_ib_i)-n\bar{A}\bar{B}}{(n-1)\sigma _A \sigma_B}$
- 0보다 크면 positively correlated, 0이면 independent, 0보다 작으면 negatively correlated
- Nominal
- Covariance Analysis ( Numeric Features)
- $Cov(A, B) = E((A - \bar{A})(B- \bar{B}))) = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}(a_{i}-\bar{A})(b_{i}-\bar{B})}{(n)} $
- $Cov(A, B) = E(A\cdot B) - \bar{A}\bar{B}$
- Correlation Analysis
Data Reduction
why? - 간단해야 효율이 좋아지기 때문
- Dimensionality Reduction - 불필요한 feature 없애기
- PCA(Principal Components Analysis) - numeric only
- Find new dimension that result in the largest amount of variation in given data
- weak 한 것은 지워버림
- Feature Selection - 중복 또는 과잉 정보 삭제
- PCA(Principal Components Analysis) - numeric only
- Numerosity Reduction(a.k.a Data Reduction)
- 데이터를 잘 나타내는 다른 data object으로 대체하기
- Parametric Method - Regression : Parameters are stored instead of data Y
- NonParametric Method
- Clustering : centroid 나 diameter만 저장
- Sampling : Stratified Sampling
Data Transformation
- Normalization
- Z - score : $z = \frac{x - \mu}{\sigma }$
- Min-max normalization : $v' = \frac{v-min_A}{max_A-min_A}(new\_max_A - new\_min_A) + new\_min_A$
- Normalization by decimal scaling : $v' = \frac{v}{10^j}$
- Discretization - numeric into intervals
- Simple Discretization : Binning
- Equal-width (distance) partitioning
- Equal-depth (frequency) partitioning - 대략 같은 수의 sample을 포함하도록
- Simple Discretization : Binning
728x90
'데이터 사이언스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Clustering 후반부 - 2단계 (2) | 2024.06.17 |
|---|---|
| Clustering 후반부 - 3단계 (1) | 2024.06.17 |
| Clustering 전반부 - 3단계 (0) | 2024.06.10 |
| Clustering 전반부 - 2단계 (2) | 2024.06.09 |
| Clustering 키워드 - 1 단계 (0) | 2024.06.09 |
